Introduction to SVG
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an XML-based image format for describing vector graphics for the web. Unlike raster images (such as PNG or JPEG), SVG graphics are scalable, meaning they can be resized without losing quality.
Basic SVG Example
Here is a basic SVG code example:
<svg width="500" height="300">
<rect x="10" y="10" width="150" height="100" style="fill:rgb(0,0,255);stroke-width:2;stroke:rgb(0,0,0)" />
<circle cx="300" cy="150" r="50" stroke="black" stroke-width="3" fill="red" />
<line x1="250" y1="70" x2="400" y2="70" style="stroke:rgb(233,115,4);stroke-width:2" />
<text x="250" y="50" font-family="Verdana" font-size="35" fill="blue">Hello Web4U</text>
<path d="M150 150 L75 250 L225 250 Z" stroke="green" stroke-width="3" fill="yellow" />
</svg>
Code Explanation:
This is a basic SVG code with various tags to draw geometric shapes and text:
- <svg>: Defines the SVG graphic area. Attributes like width and height set the size of the canvas area.
- <rect>: Draws a rectangle. The width and height attributes define the size, and the style attribute is used for colors and borders.
- <circle>: Draws a circle. The cx and cy attributes set the center position, r sets the radius, stroke sets the border color, stroke-width sets the border thickness, and fill sets the fill color.
- <line>: Draws a straight line between two points defined by x1, y1 and x2, y2 attributes.
- <text>: Draws text in the SVG area. The x and y attributes set the position of the text, and the font-family, font-size, fill attributes define the style of the text.
- <path>: Draws a custom shape using the d attribute, which contains a sequence of commands to draw lines and curves.
Result in Browser
When this code is displayed in a browser, the result will look like this:
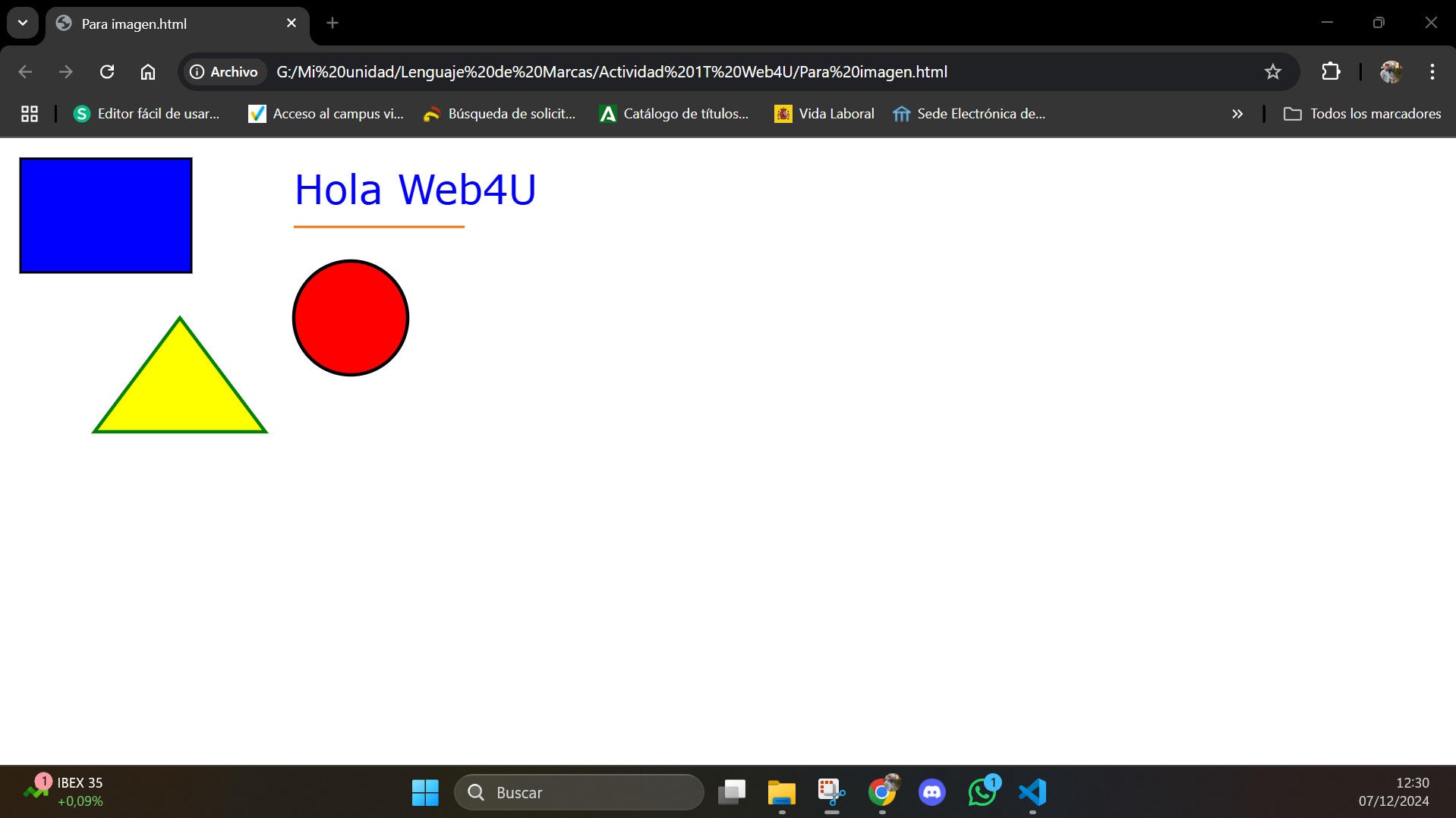
Useful Links
For more details about SVG features, visit the W3C Official Page.
You may also find the W3Schools SVG Tutorial helpful.

